Beckhoff ADS
ADS is a network protocol built by Beckhoff Automation GmbH and is used in their Industrial PCs to read and write from and to PLC variables.
With the Namespace discovery feature, all available Signals can be discovered.
ADS Router
If the PLC and hopit Edge are running on different devices, an ADS Route between the PLC and the device hopit Edge is running must be added.
For this, the ADS Router service in hopit Edge must be enabled and a unique AMS Net Id must be configured.
Corresponding Edge configuration and Device Twin definition to activate the ADS Router service:
- Edge-UI
- Device Twin
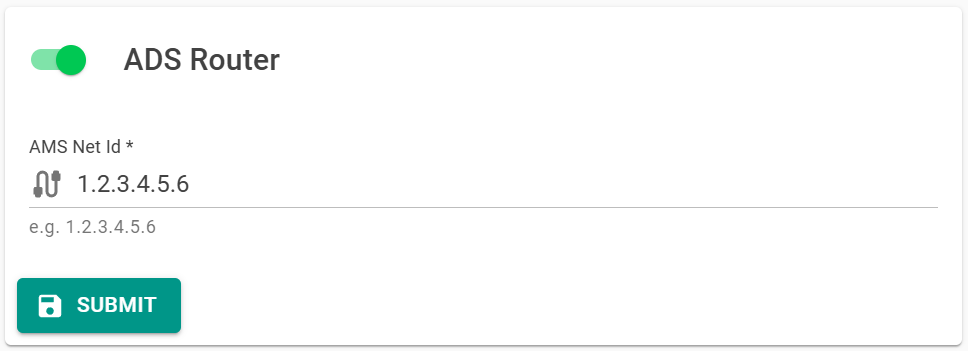
{
"AdsRouter": {
"AmsNetId": "1.2.3.4.5.8",
"Enabled": true
},
}
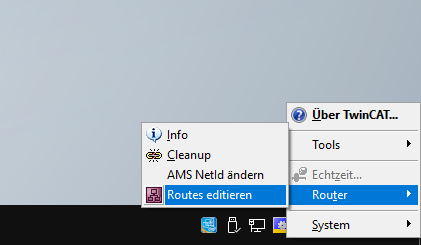
Additionally, a route from the Beckhoff IPC to the hopit Edge device must be added on the IPC. This can be done on the Beckhoff IPC by clicking on the TwinCAT Runtime* symbol in the Windows Taskbar -> Router -> Edit Routes.
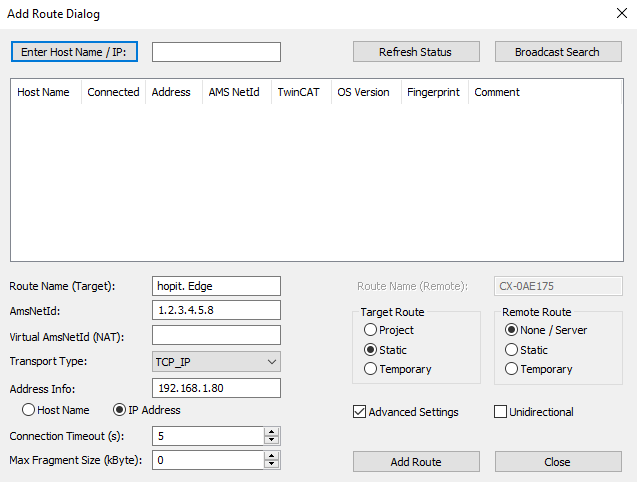
Now the route can be added with an arbitrary Route Name, the AmsNetId configured in hopit Edge, the IP Address or Host name of the Edge device. The Remote Route option can be set to None/Server.
You can keep the ADS router service disabled if you have the XAR also installed on the computer which runs hopit Edge. Then you can configure a route between these two XAR's.
Use the Ams Net Id from the XAR you want to read data from and leave the Host parameter empty in the Target settings (see next section).
Configuration
The ADS Target has the following parameters:
AmsNetId: The AMS Net Id of the PLC.Port: AMS Port. Default is851.Host: Host name or IP Address of the IPC. This must benullwhen theAmsNetIdis the local address127.0.0.1.1.1.TargetType: The type is alwaysADSfor this Target.
For the common parameters, see the Introduction.
Corresponding Edge configuration and Device Twin definition to activate the ADS Target service:
- Edge-UI
- Device Twin
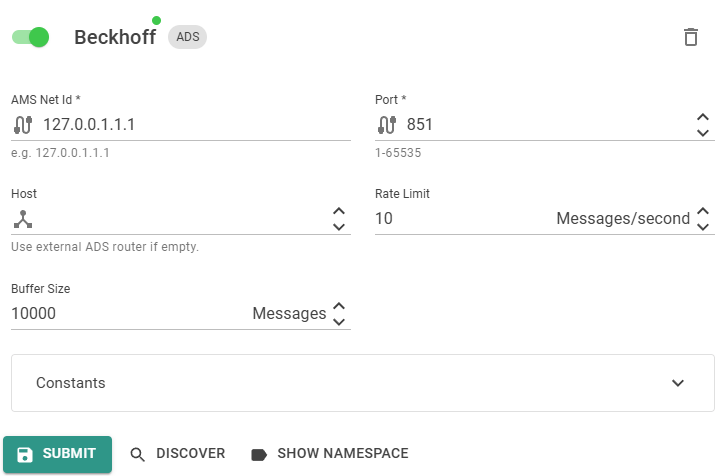
Beckhoff is in this example the Name of the Target. This can be any unique name.
{
"Beckhoff": {
"Port": 851,
"AmsNetId": "127.0.0.1.1.1",
"Host": null,
"TargetType": "ADS",
"MessagesPerSecondLimit": 50.0,
"BufferSize": 1,
"Constants": {},
"Enabled": true
}
}
Data Streaming
Every basic data types, ENUM's, arrays, structures or aliases can be handled. Also nested structures, structures of arrays, arrays of structures and multidimensional arrays are supported.
The Signals to read or write are configured in the Router.
Examples for reading signals from this TwinCAT structure:
TYPE ST_Polygonline:
STRUCT
EndPoints : ARRAY [1..2] OF INT;
Properties : ST_PolyProperties;
END_STRUCT
END_TYPE
TYPE ST_PolyProperties:
STRUCT
Name : STRING(35);
Length : INT;
END_STRUCT
END_TYPE
places in the GVL list with the name Polygonline results in the signal names:
GVL.Polygonline: reading the whole structure. This will return the signals:GVL.Polygonline.EndPoints[1]GVL.Polygonline.EndPoints[2]GVL.Polygonline.Properties.NameGVL.Polygonline.Properties.Length
GVL.Polygonline.EndPoints: This will return the signals:GVL.Polygonline.EndPoints[1]GVL.Polygonline.EndPoints[2]
GVL.Polygonline.EndPoints[2]GVL.Polygonline.Properties.Length
Signals can be also read with Regex matcher. See the Router documentation for details.
Signal discovery is available for this Target. See the Introduction for more details.
For information how signals are named and labeled in Data Lakes, please read the Data Lake documentation.